Deferred liability definition
/What is a Deferred Liability?
A deferred liability is an obligation for which settlement is not required until a later period. This usually means that the business has been paid by a customer for the delivery of goods that have not yet been delivered, or for the performance of services that have not yet been performed.
Accounting for a Deferred Liability
When a business receives cash in exchange for a future obligation, it records a debit to the cash account and a credit to the deferred liability account. When it eventually completes its obligations related to the payment, it debits the deferred liability account and credits the related revenue account.
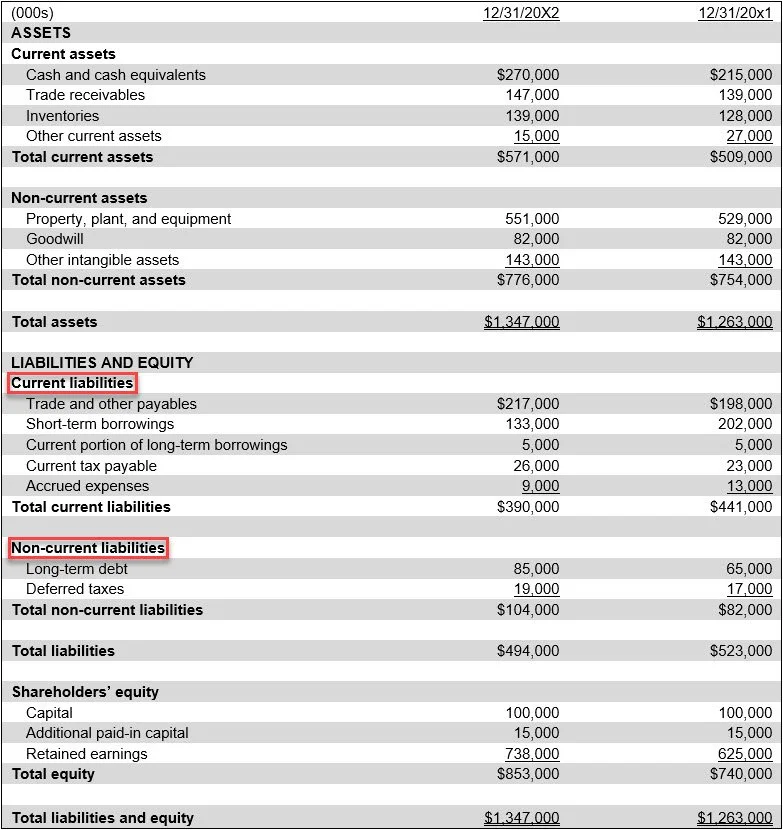
Presentation of a Deferred Liability
If a deferred liability is not to be settled for more than one year, then it is classified on your balance sheet as a non-current liability. If the settlement date is within one year, then it should instead be classified as a current liability. These two classifications are shown in the following balance sheet exhibit. Deferred liabilities are rarely labeled as such on the balance sheet; instead, they are included in other line items.
Related AccountingTools Course
FAQs
How Do Deferred Liabilities Affect Financial Ratios?
Deferred liabilities increase a company’s total liabilities, which can raise its debt-to-equity and debt-to-assets ratios, indicating higher financial leverage. This may suggest greater long-term obligations and potentially increased financial risk. Additionally, high deferred liabilities can impact credit evaluations and investment decisions by signaling future cash outflows.